About NCI-H441
The NCI-H441 cell line is derived from human epithelial adenocarcinoma and was established in 1982 from the pericardial fluid of a male patient diagnosed with papillary adenocarcinoma of the lung. Since its establishment, NCI-H441 cells have been extensively studied to gain insights into the molecular characteristics and signaling pathways associated with lung adenocarcinoma. One notable feature of NCI-H441 cells is their hyperdiploidal karyotype, with a modal chromosome number of 52. In addition, a high frequency of cells (4.9% of total observed cells) exhibits chromosome counts of 53, indicating chromosomal instability in this cell line. Notably, structurally normal N13 and N14 chromosomes are consistently absent in all cells. These chromosomal abnormalities contribute to the genetic complexity and heterogeneity observed in lung adenocarcinoma.
NCI-H441 cells express mRNA and proteins of SP-A, which is the major surfactant-associated protein found in the lungs. SP-A is involved in pulmonary surfactant homeostasis and plays crucial roles in lung development, innate immune defense, and modulation of inflammation. The expression of SP-A in NCI-H441 cells reflects their origin from the lung epithelium and underscores their potential relevance as a model for studying lung adenocarcinoma.
In terms of drug efficacy, NCI-H441 cells exhibit broad resistance to kinase-targeted agents, which are designed to inhibit specific signaling pathways involved in cancer cell growth and survival. However, a notable exception is observed with agents acting on MNK1/2. The MNK1/2 pathway is part of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling cascade and plays a role in protein synthesis, cell proliferation, and survival. The sensitivity of NCI-H441 cells to MNK1/2-targeted agents suggests that this pathway may be a potential therapeutic target in lung adenocarcinoma treatment.
NCI-H441 Tumor Kinetics in the SRG™ Rat
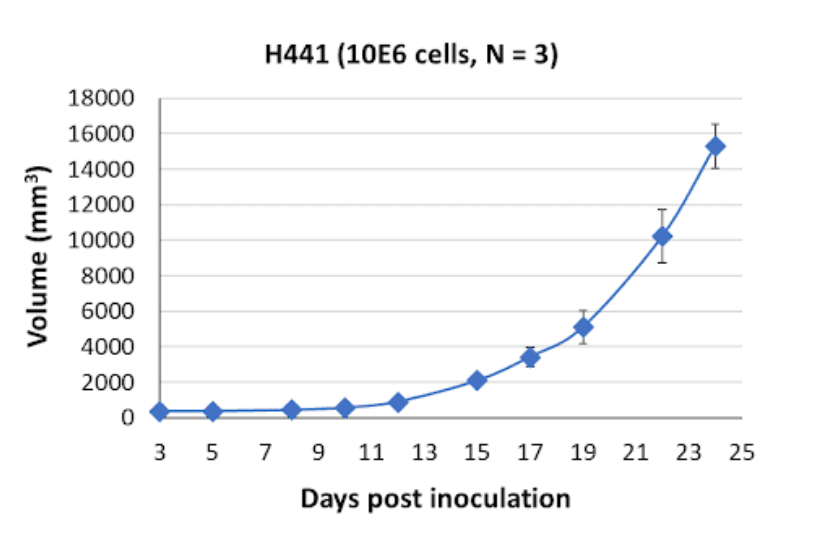
When xenografted into SRG rat models, NCI-H441 cells produce fast-growing, cystic, and highly friable tumors. The rapid tumor growth and the presence of cystic structures within the tumors recapitulate the aggressive nature of lung adenocarcinoma. The friable nature of the tumors suggests a delicate tumor structure prone to fragmentation.
Products & Services
Xenograft Efficacy Studies
Includes collection of blood, tissues & tumor for ADME, PK/PD and analysis.
(Bi)weekly Tumor Sampling
Via fine needle aspiration (FNA). For longitudinal evaluation of drug exposure, histology and gene expression.
OncoRats
Cutting edge models optimized for engraftment.
Get help with your research by scheduling a call with Hera.

References (MLA):
- Depicolzuane, Lynnlee, et al. “Surfactant Protein-a Function: Knowledge Gained from SP-a Knockout Mice.” Frontiers, 3 Dec. 2021, www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fped.2021.799693/full.
- Joshi, Sonali, and Leonidas C Platanias. “MNK Kinase Pathway: Cellular Functions and Biological Outcomes.” World Journal of Biological Chemistry, 26 Aug. 2014, www.wjgnet.com/1949-8454/full/v5/i3/321.htm.
- Liehr, Thomas, et al. “Small Supernumerary Marker Chromosomes Derived from Chromosome 14 and/or 22 – Molecular Cytogenetics.” Molecular Cytogenetics Logo Molecular Cytogenetics, 25 Feb. 2021, molecularcytogenetics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13039-021-00533-6.
- Luquet, I, et al. “Hyperdiploid Karyotypes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Define a Novel Entity: A Study of 38 Patients from the Groupe Francophone de Cytogenetique Hematologique (GFCH).” Nature News, 11 Oct. 2007, www.nature.com/articles/2404974.
- Yamaoka, Toshimitsu, et al. “Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Targeted Cancer Therapy.” MDPI, 6 Nov. 2018, www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/19/11/3491.
