Creating Humanized MDCK Cell Lines for Transporter Assays
Because of the potential for endogenous canine transporters to interfere in membrane transport assays in the canine MDCKII cells, Hera set out to conduct genome engineering to knock out and introduce the human versions of the genes. MDCK canine cells are desired for easy handling and a high proliferation rate. MDCKII cells form monolayers for transporter assays in 3 days vs Human Caco-2 cells take 21-days.
Hera Biolabs has generated cPgp/cBcrp double knockout MDCKII cell line (MDCKII-BP-null), and humanized cell lines stably expressing ABCB1 (MDR1) gene encoding hPgp and ABCG2 gene encoding hBCRP on the MDCKII-BP-null cell background (hMDR1-MDCKII-BP-null and hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null).
Application: (1) MDR1 or BCRP substrate assessment; (2) MDR1 and BCRP inhibitor assessment.
Creating Double KO MDCK-II cells
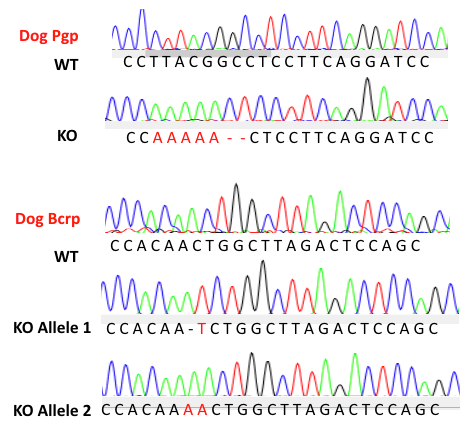
Hera’s nuclease technology (Cas-CLOVER) was used to introduce frameshift mutation on cPgp and cBcrp gene leading to premature stop codons downstream in early exons.
Multidrug Resistance Direct Dye Efflux Assay
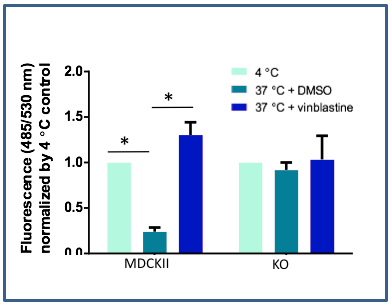
Transport activity of cPgp and cBcrp was abolished in MDCKII-BP-null cells. The Pgp and Bcrp activity to transport substrate DiOC2(3) were detected by Multidrug Resistance Direct Dye Efflux Assay (ECM910, Millipore).
hMDR1/hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null cell pool characterization
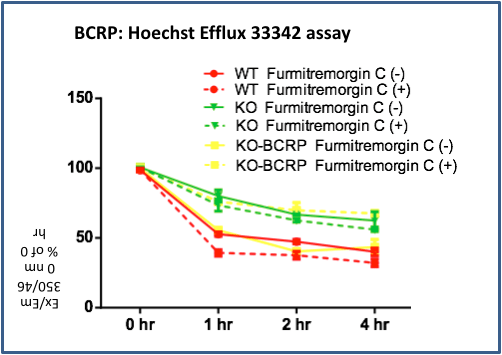
MDCKII WT, MDCKII-BP-null (KO) and hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null (KO-BCRP) pool cells were incubated with 5 μM Hoechst for 1 hour at 37°C (before effluxing). Then cells were switched to Hoechst-free medium with/without BCRP inhibitor Fumitremorgin C for 1, 2 and 4 hours. Hoechst remaining in the cells was measured in a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Ex/Em=350nm/460nm), and was expressed as percentage of the value determined after 1 hours of incubation. hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null cells pool show BCRP-mediated efflux as BCRP specific inhibitor Fumitremorgin C inhibits the efflux.
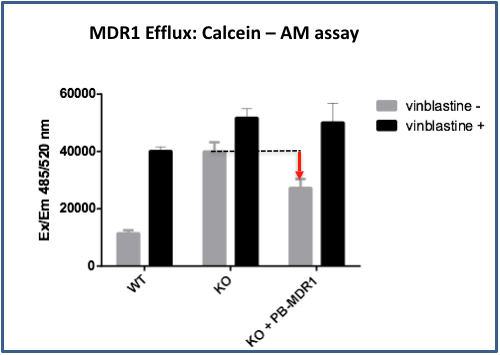
MDCKII WT, MDCKII-BP-null (KO) and hMDR1-MDCKII-BP-null (KO+ PB-MDR1 pool cells were incubated with 5 μM Calcein AM for 1 hour with/without MDR1 inhibitor vinblastine. Calcein-AM accumulating in the cells was measured in a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Ex/Em=485nm/520nm). Compared to MDCKII-BP-null cells, hMDR1-MDCKII-BP-null cells show lower Calcein-AM accumulation, indicating possible human MDR1 activity.
hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null cell clonal line characterization
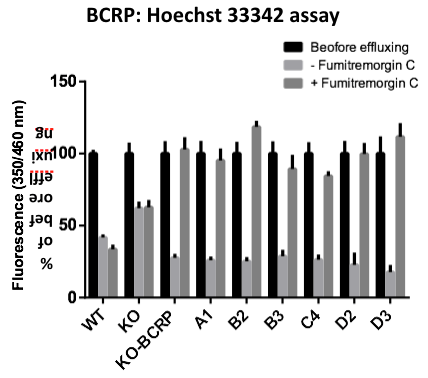
MDCKII WT, MDCKII-BP-null (KO), hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null pool (KO-BCRP) and individual clones (A1, B2, B3, C4, D2, D3) cells were incubated with 5 μM Hoechst for 1 hour at 37°C (before effluxing). Then cells were switched to Hoechst-free medium with/without Bcrp inhibitor Fumitremorgin C for 1 hours. Hoechst remaining in the cells was measured in a fluorescence spectrophotometer (Ex/Em=350nm/460nm), and was expressed as percentage of the value determined after 1 hours of incubation. Multiple MDCKII-KO-BCRP single cell colonies show BCRP-mediated efflux (because BCRP specific inhibitor Fumitremorgin C inhibits the efflux)
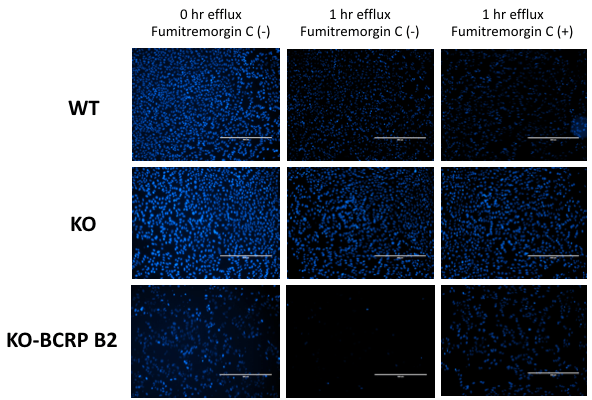
Cell imagines of MDCKII cells in Hoechst efflux assay. Hoechst dye binds to the cell nucleus (blue). MDCKII WT cells (WT) efflux Hoechst dye (blue intensity decrease) through transporters other than canine Bcrp, because Bcrp inhibitor Fumitremorgin C did not inhibit the efflux. MDCKII-BP-null (KO) cells show much lower efflux activity. hBCRP-MDCKII-BP-null (KO-BCRP B2) cells show obvious dye efflux which is inhibited by BCRP inhibitor, indicating the human BCRP contributes the efflux.
